Is Liver Disease Harmful?
Parasitical Worms.com The liver fluke Fasciola hépatica has been known since the eighteenth century. This parasite is parasitic in bile ducts and causes liver disease mainly in ruminant animals such as buffaloes, cows, etc., is less parasitic and causes disease in humans.
Flukes of the liver are also able to move astray to the parasite in many different places in the body of the host such as peritoneum, vein or subcutaneous organization
Pictures of large liver fluke
……………………………………………
I. Epidemiology
Fasciola hépatica was discovered by Lannea in 1758 in Japan, endemic in several Asian countries (Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, China, Korea, Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, Philippines .
 . In Vietnam, fascioliasis has been detected in 45 provinces with about 4500 patients.
. In Vietnam, fascioliasis has been detected in 45 provinces with about 4500 patients.II. The development cycle of the big liver fluke:
The intermediate hosts of the liver fluke are Lymnaea viridis and L.swinhoei snails. Different from small liver fluke, the intermediate host is melania tuberculata
Flukes are mainly found in herbivores such as buffaloes, cows, cats, dogs and sheep People are just random hosts when accidentally eating aquatic plants such as cilantro, cilantro, cilantro, watercress, or drinking water contaminated with uninfected tapeworm larvae.
Leaf-shaped liver flukes are about 30 x 10-12 mm in size, and eggs are about 140 x 80 mm. In the natural environment, the tapeworm eggs open into parasitic hairy larvae in snails and then develop into tail larvae. The caudal larvae leave the snail in water and attach to aquatic plants to become cysts.
 .
.People who eat these cysts will get sick. After entering the stomach, duodenum, the capsule shells are destroyed and the larvae are released, the larvae penetrate the duodenum into the abdominal cavity and move to the liver, the larvae puncture the liver envelope and enter the liver parenchyma to growth and development there they release toxins that destroy liver parenchyma.
.
Ultrasound images of tapeworm larvae cause necrosis of liver parenchyma
However, there are very few cases where the larvae move astray, they do not go to the liver but to some other organs such as skin, muscle, joints, breast, stomach wall .. and cause disease there. In Vietnam, there have been cases such as tapeworm infection in the knee joint, in the breast, or causing a colon tumor misdiagnosed as colon cancer.
After a period of 2-3 months developing in liver parenchyma, adult flukes entering the bile ducts continue to grow and lay eggs there. For a long time of about 10 years, if left untreated, it will lead to biliary tract cancer.
 .
.Flukes of the liver in biliary tract
+ The disease is found at any age: 4 - 80 years old - the most infected age is 30-40 years old.
+ Women are 2 to 25 times more infected than men
+ The disease is not evenly distributed depending on the locality, eating habits and people's understanding.
III. Clinical symptoms
It is difficult to know without clinical symptoms, or poor symptoms. Clinical symptoms are also usually not as aggressive as other liver apks.
* Functional symptoms:
+ Abdominal pain: often dull ache, unknown location
+ Right lower quadrant pain: mild pain, rarely severe pain, accounting for 70-80% of cases
+ Gastrointestinal disorders: diarrhea, diarrhea, loss of appetite
* Systemic symptoms:
+ Fatigue: very common
+ Fever: may have a high fever, or just a mild fever, very common in 60-70% of patients.
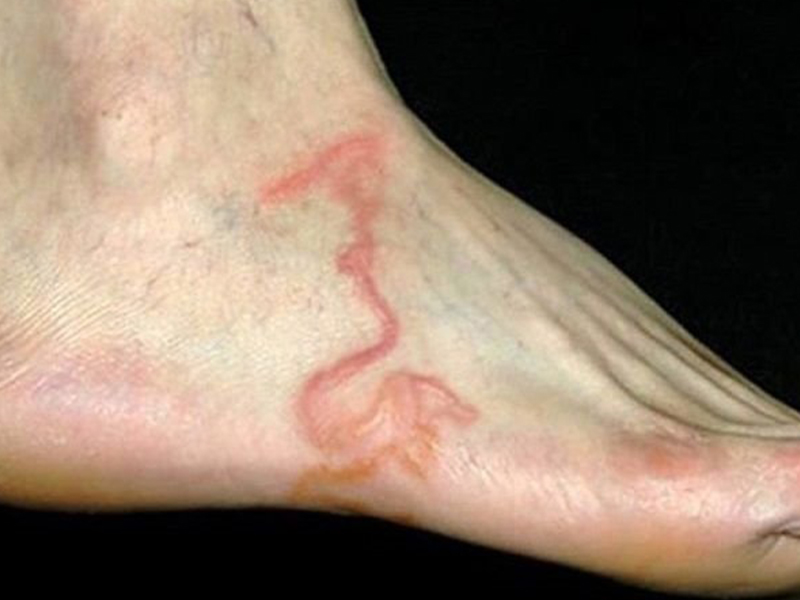
+ Skin allergy: seen in 20-30% of patients, manifested nodules on the skin mainly in the thighs, buttocks, back, tingling sensation, pen guilt, discomfort ...

Subcutaneous bruising in patients tested for infection with massive liver fluke
* Other less common symptoms:
- Prolonged cough, chest tightness
- Jaundice: common when the flukes move into the bile ducts and develop there causing biliary tract inflammation.
* Physical examination:
+ Hepatomegaly: only about 2-3cm below the ribs, painful or intercostal pressing, painful hepatomegaly only in 20% of cases.
+ Spleen large: very rare
+ Gallbladder: never big
IV. Subclinical symptoms:
- Complete blood count: leukocytosis increased, anemia, especially eosinophilia increases, occurs in 90% of cases
- Flukes in faeces: only when the worms enter the bile ducts and lay eggs there will find flukes in the stool, even in this case, it is not 100% found in the liver fluke due to small egg laying. , so have to find many times (3 times in a row), need to pay attention to confusion with eggs of other helminths. In some cases, a duodenum aspirator is required to find an egg.
- Liver function; Transaminases may increase but only 2-3 times. The percentage of people with transaminases is very low
- Immune reaction: the simplest and most reliable method is the ELISA method. When the flukes invade the liver parenchyma, they secrete the most antigens, 2 weeks after the onset of antibody is shown as IgG and IgE.
 . In addition to the ELISA method, there are other methods such as erythrocyte agglutination, immune electrophoresis but low sensitivity and specificity. It should be noted 6 months after recovering from ELIS. . Dịch vụ: Thiết kế website, quảng cáo google, đăng ký website bộ công thương uy tín
. In addition to the ELISA method, there are other methods such as erythrocyte agglutination, immune electrophoresis but low sensitivity and specificity. It should be noted 6 months after recovering from ELIS. . Dịch vụ: Thiết kế website, quảng cáo google, đăng ký website bộ công thương uy tínRelated news
-
 Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ...
Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ... Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ...
Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ... Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ...
Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ... Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ...
Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ... Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ...
Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ... Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ...
Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ... MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ... CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...
CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...





