Outdoor Tube Infection By Infection (otomycosis)
Fungal ear infections are a peripheral, non-contagious fungal disease in which the invasive epidermis causes acute or chronic inflammatory manifestations of the outer ear canal and can affect the eardrum. ...
1
Fungal ear infections caused by 10% of cases of otitis media in general and are common in humid climates such as tropical and subtropical countries.
In temperate regions, the frequency of illness increases in the summer. More than 50 types of fungi related to the disease, the most common are Aspergillus (80% - 90%, A
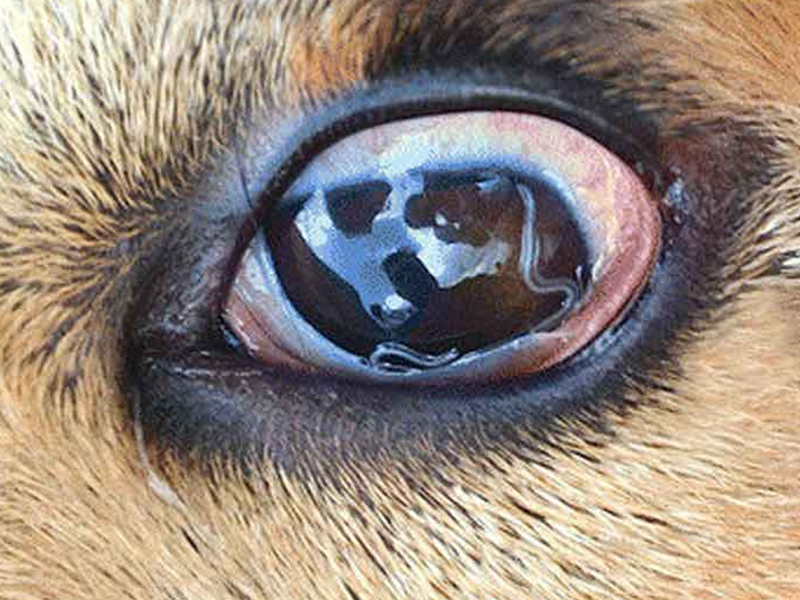 .tropicalis), Actinomyces. Trichophyton.
.tropicalis), Actinomyces. Trichophyton.In adults, the disease is distributed among all ages, male and female, but is less common in children. The disease usually develops after an infection of the outer ear canal caused by bacteria treated on the spot with corticosteroids, or after an injury such as a scratch caused by the removal of ear wax with a match, a hairpin, etc. In swimmers, heavy sweating as well as cases of eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis of the sebaceous gland in the ear canal are also considered extradition factors
2 CLINICAL EXTREMELY INFECTION
95% of cases of fungal ear infections occur after infections of the outer ear canal, so the manifestations of pain, itching, and discharge of bacterial ear infections are similar to those of external ear infections. due to bacterial agents.
In the acute form, the onset is sudden with severe ear aches, especially when swallowing, swallowing heavily. The secretions may be foul or odorless, the color changes depending on the pathogen, may be white, black, gray or yellow .
 ... The black secretion found in Aspergillus niger infection, ivory-white as usual cheese due to Candida spp; If combined with germs, there will be pus or blood.
... The black secretion found in Aspergillus niger infection, ivory-white as usual cheese due to Candida spp; If combined with germs, there will be pus or blood.The itchy feeling inside the ear canal causes much discomfort for patients The inflammation causes the epidermal cells to flake more, clumping with the fungus and other components that form the earwax to obstruct the lumen and lead to hearing loss. Otoscope examining the ear canal showed redness, edema and exudation.
On a wet earwax, the fungus grows in clumps of ivory-white or fluffy, sometimes green or black spots on the surface. lymph nodes or around the ears are also observed in some cases, especially when infected with bacteria.
Contrary to exacerbations, pruritus is a major symptom of the chronic form, with an unspecified inflammation, and inadequate fluid secretion. Examination of the ear canal will observe the flaking image of the dermis of the epidermis covering the congested, necrotic skin.
 . Fungi do not invade the eardrum but inflammation of the eardrum granules can occur and cause perforation of the eardrum when the disease is prolonged, untreated. However, complications of chu4m osteoarthritis after perforation of the eardrum are rare
. Fungi do not invade the eardrum but inflammation of the eardrum granules can occur and cause perforation of the eardrum when the disease is prolonged, untreated. However, complications of chu4m osteoarthritis after perforation of the eardrum are rare3. DIAGNOSTIC INFECTION OF INFECTIONS
Differential diagnosis
It is important to distinguish between fungal ear infections caused by bacteria, seborrheic dermatitis, or contact dermatitis. Signs of non-response to topical antibiotics and corticosteroids as well as sudden hearing loss are suggestive of fungal pathogens.
Microbiological diagnosis
Samples are earwax or secretions taken by an ear, nose and throat doctor in an indispensable condition. The specimen is stored in a sterilized vial and sent to the laboratory as soon as possible.
Direct observation
On wet smears of the specimen with 10% KOH, yeast seed cells will sprout and fungal hyphae when infected with Candida sp. If mycelial infection is observed, transparent mycelium is transparent, branched, with or without walls, and the identification should be based on culture.
The reproductive structures of fungal filaments are sometimes found and this allows a preliminary identification of the pathogen as in the case of Aspergillus spp.
 with sporotomic stem cell attachment.
with sporotomic stem cell attachment.When suspected of co-infection with bacteria, additional Gram stain specimens should be performed to identify bacilli or cocci, Gram (+) or Gr (-).
Transplant
Fungal identification: most of the fungi that cause external ear infections are sensitive to cycloheximide, so the best fungal culture environment is Sabouraud chloramphenicol and incubated culture. After 3-4 days, observing the fungus with the naked eye and under a microscope will help identify the fungus.
Bacterial identification and antibiotic mapping are sometimes necessary to select the appropriate antibiotic in cases of mixed lung infections or secondary fungal infections after a chronic bacterial infection. Samples were cultured on nutrient agar, blood agar or soy tryptose agar (tryptose soybean agar) .. and incubated at 370C. After the bacteria grow into a cyst, the identification is based on biochemical reactions.
 .
.4. TREATMENT FOR EXTERNAL HEART DISEASE
After washing the ears with hydrogen peroxide or 5% aluminum acetate solution to reduce edema and remove wax, topical treatment with 2% acetic acid solution or a mixture of alcohol - white vinegar (1: 1 ratio) will have the effect of killing bacteria, fungi.
If the acidification of the ear canal is not effective hanging (100,000 units / ml) or ointment form (200,000 units / g) days. . Dịch vụ: Thiết kế website, quảng cáo google, đăng ký website bộ công thương uy tín
Related news
-
 Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ...
Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ... Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ...
Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ... Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ...
Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ... Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ...
Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ... Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ...
Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ... Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ...
Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ... MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ... CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...
CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...






