Parasitic Meningitis
1. The concept of meningitis and parasitic meningitis
1. 1. Meningitis?
Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the spinal cord and brain, collectively called the meninges. Common agents of meningitis include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites
1.2
Parasitic meningitis is one of the most common causes of eosinophilic meningitis, the cause of which is a parasite People with eosinophilic meningitis are when the body has more than 10 eosinophils / mm3 of CSF or eosinophilic components accounting for more than 10% of the cells in the CSF. The source of infection is mainly through the gastrointestinal tract by eating raw foods containing pathogens, less frequently, the parasite can pass through the skin when people are in contact with soil or workplace where germs are present.
 . .
. .Parasites known to be associated with meningitis include: pinworms (Angiostrongylus cantonensis), dendritic worms (Gnathostoma spinigerum), schistosomiasis (Schistosoma haematobium), cysticercosis (Cysticercus cellulosae), roundworms dog / cat (Toxocara canis / Toxocara catis), and fluke (Paragonimus westermani).
Commonly found in Pacific islands, Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean. There are also in Japan and China.
3
31. Worm disease
Worms (Angiostrongylus cantonensis) are the most common cause of parasitic meningitis. Pinworm larvae have a neurophilic nature.
Reservoir: Rats (Bandicota and Rattus species).
 . The vermin that parasitize the pulmonary arteries of mice should be called "rat lungworms," which lay eggs in arteries and hatch into stage 1 larvae. The lungs then migrate up to the bronchi and then to the intestine, excreted in the stool.
. The vermin that parasitize the pulmonary arteries of mice should be called "rat lungworms," which lay eggs in arteries and hatch into stage 1 larvae. The lungs then migrate up to the bronchi and then to the intestine, excreted in the stool.Humans: eat snails that have uncooked larvae or eat raw vegetables that are sticky with mucus produced by snails or other mollusks. In the intestine, larvae travel through the intestinal wall and move into the brain and spinal cord, causing meningitis (but very rarely cause damage to the spinal cord and brain parenchyma) and to the eyes, causing impaired vision or blindness eye.
Symptoms: Eosinophilic meningitis is usually seen after 2 weeks and dies at only 2-3%. In humans, on the surface of the brain and spinal cord, the parasite becomes terminal larvae that cannot develop into adult worms like in mice. Another type of vascular worm, Angiostrongylus costaricensis, parasites in small intestinal mesenteric arteries in the ileum region, causing ileoceal intestinal colitis for rats who are the final hosts.
3.2.
 . Disease caused by dendritic worms
. Disease caused by dendritic wormsThe dendritic worm larvae can travel under the skin, reaching organs, the nervous system and the eye sockets.
Reservoir: Pigs, dogs, cats .. This is an animal-to-human disease that attaches to the intestinal wall of some animals such as pigs, dogs and cats, which are then excreted into feces and then developed into embryos. In water, they develop inside intermediate hosts (fish, frogs, clones, water snakes).
Humans: when eating foods made from poultry, fish, snakes carrying larvae or drinking water with uncooked larvae.
3.3. Diseases of dog roundworm and cat roundworm
Reservoir: Dogs and cats.
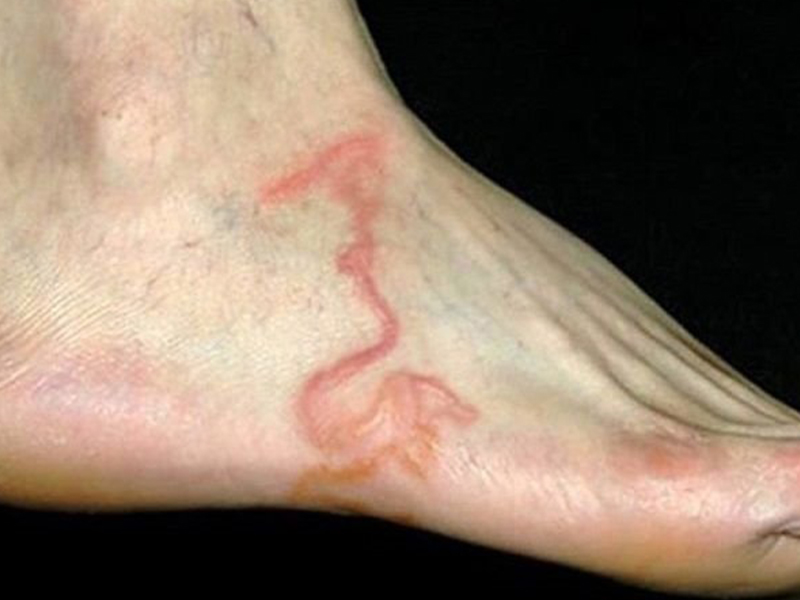
Humans: Eating food contaminated with worm eggs (brought by flies), or worm eggs from the hands by contact with the soil but not washed before eating. In the human body, larvae of dog roundworm and cats can move to many different areas, to any area, there are symptoms in that area.
Symptoms: itchy skin, liver swelling, pericardial or pleural effusion, blindness and meningitis.
3.4. Cysticercosis
Life cycle of a tapeworm parasite: adult tapeworms parasitize in the small intestine of humans (the last host), producing eggs carrying embryonic cells and excreting faeces, when pigs are ingested ( Pigs are intermediate hosts) When the eggs come into the gut, the larvae penetrate the intestinal wall to move throughout the body of the pig, they often nest in lean pork fibers to form tapeworms (rice disease / rice pig).
Humans: Eat raw "pork rice" (nem chua) or re-cooked, the larvae will then develop into adult flukes in the small intestine. Or eating the uncooked food contaminated with tapeworm eggs carrying embryonic cells from the outside environment will cause cysticercosis In humans: from within the intestine, the tapeworm larvae penetrate the vascular wall into the bloodstream and migrate to all over the body causing hard bumps in the muscles, most commonly in the subcutaneous tissue, brain and eye. In this case, the person is the intermediate host.
 .
.Symptoms: brain damage with seizures, vision loss or blindness ...
4. Symptoms of parasitic meningitis
The most common symptoms are fever and headache (seen in more than 90% of patients, often with pain. . Dịch vụ: Thiết kế website, quảng cáo google, đăng ký website bộ công thương uy tín
Related news
-
 Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ...
Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ... Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ...
Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ... Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ...
Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ... Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ...
Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ... Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ...
Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ... Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ...
Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ... MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ... CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...
CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...





