Where Are The Diseases From Infectious Diseases?
Parasitical Worms.com Parasites are excreted according to faeces into the external environment, including parasites in humans and parasites in animals that transmit and infect humans.
Most parasites are excreted in faeces as parasites in the small intestine or large intestine, but there are also some parasites in the liver, lungs, mesenteric veins are also excreted pathogens in the stool. Some common parasites in humans and animals excreted as faeces can be listed as follows:
The parasite exits in human feces
Unicellular
Entamoeba histolytica: cysts are formed in the intestine and follow the stool to the outside. Cysts have thick walled cysts that can survive long on the ground, underwater
Giardia lamblia: cysts are excreted in faeces, can spread by water, infect people through food and drinking water.
Crptosporidium spp: follicular eggs formed by sexual cycle in the host's small intestine and excreted in the faeces
Worm parasites
Ascaris lumbricoides roundworm: Ascaris round eggs have very thick crust, very high resistance to the external environment Fecal discharge eggs may disperse in soil or flow in water. The person infected when swallowing the egg has an embryo inside.
 .
.Trichuris trichiura: Trichuris is distributed in the same context as roundworm eggs.
Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator ameericanus: hookworm eggs, when excreted, need soil with enough oxygen, heat and humidity to hatch eggs outside the soil. Hookworm eggs do not hatch larvae when submerged above 20 cm and hookworm larvae do not exist in water. People infected by hookworm larvae burrow through the skin.
Strongyloides stercoralis Strongyloid larvae of eel worms are excreted in the faeces and will develop in two directions depending on the climate and external temperature
Flukes parasites
Tapeworm taenia solium and T. saginata: Burn old flukes (also known as egg-carrying tapeworms) of tapeworm tapeworms and cow excreta. In the environment, the decayed flukes release the eggs out.
Pigs or cows roam, eat grass in the field to swallow tapeworm eggs, or beef (or swallow unbroken flukes) pigs (tapeworm larvae) or beef rice (tapeworm larvae).
 .
.The people who eat pork, cows have live tapeworm larvae will get tapeworm or tapeworm. The tapeworm eggs can also disperse in the stream of water in case of flooding or raining.
Fluke. All parasitic flukes and human pathogens are parasites of animals and animals are the main parasite containing fluke The tapeworm eggs are excreted in the faeces into the water to hatch, so the fluke spreads mainly by human faeces discharged directly into the water.
Schistosomiasis: A schistosomiasis should also be excreted into the water in order to continue growing.
Parasites discharge according to animal feces transmitted to humans.
Balantidium coli: is the main parasitic hair in pigs, cysts are excreted in pig excreta and dispersed outside by pigs roaming, and cleaning water is discharged freely without treatment. physical.
Cryptosporidium: Cysts are excreted in feces of cats and dogs.
 .
.Toxoplasma gondii: Cats are the only host of T. gondii, follicular eggs are excreted in cat feces
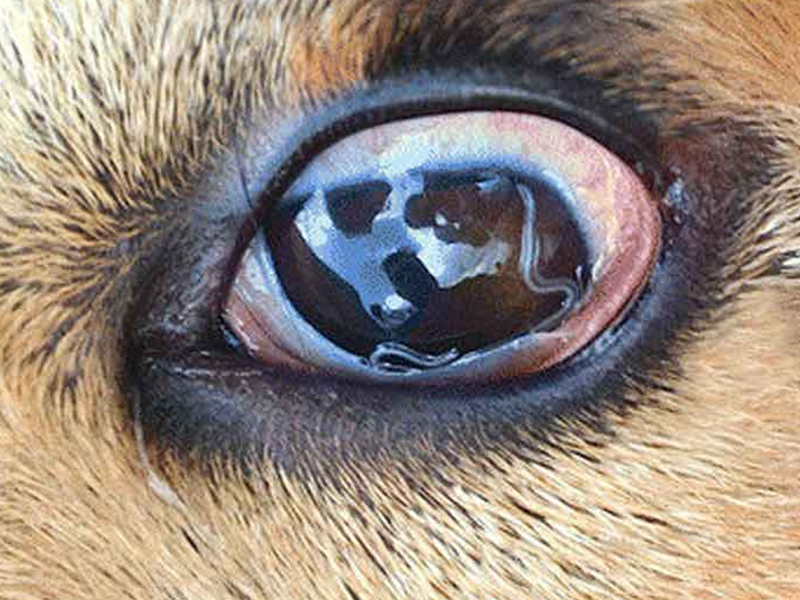
Toxocara spp, parasitic worms in the small intestine of cats and dogs, lay eggs according to their faeces, spread in the soil or follow rain water, wash floor water of dogs and cats defecate.
Cat hook, Ancylostoma app parasitize the small intestine of dogs and cats, lay eggs in the feces out, eggs hatch larvae on the ground and re-enter the dogs and cats through the skin. People infected by dog and cat larvae infiltrate through the skin.
Flukes, as stated above, all types of tapeworms infected by humans are animal parasites such as the intestinal flukes of Fasciolopsis buski, which are parasitic in pigs, and large liver flukes Fasciola spp. water buffaloes, sheep… small liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini are found in dogs, cats, mice, and other fish-eating species.
The spread and spread of parasites are excreted in faeces in human habitats.
Parasites in human and animal faeces are spread in a wide or narrow landscape depending on the type of parasite, human excretion habits and animal feeding practices. Human and animal feces can be released on soil or into the water from which it is released and spread in many ways.

The parasite spreads according to the litter on the ground.
Manure excreted on the ground usually occurs in large spaces such as gardens, fields, agricultural plantations, industrial plants, etc. The faeces can be completely discharged on the ground or locked up. temporary way. In sunny weather, feces can dry out and swell away with the wind.
In case of rain, feces will be washed away by the flow of rainwater. Case. . Dịch vụ: Thiết kế website, quảng cáo google, đăng ký website bộ công thương uy tín
Related news
-
 Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ...
Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ... Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ...
Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ... Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ...
Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ... Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ...
Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ... Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ...
Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ... Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ...
Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ... MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ... CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...
CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...






