Worm Infestation Situation
Main events:
Earthworm infestation is caused by a number of different helminth species;
They are transmitted via eggs from the faeces of infected people into the soil and toilets are quite poor;
Approximately 1.5 billion people globally are infected with soil-transmitted helminths;
Infection with soil-transmitted helminths will lead to nutritional and physical depletion in children;
Preventing worm infection based on: Periodic worm books to eliminate and prevent re-infection, enhance health education to prevent, improve hygiene and living conditions to reduce infections into contaminated soil and eggs Use safe and effective medicines to control the infection.
Earthworm infestation is one of the most common infections in the world and affects the poorest and most extreme communities. They are transmitted by eggs contained in human feces and thus contaminate soil in areas of poor sanitation and living conditions. The main species that infect humans are roundworm, hairworm, and hookworm
Distribution and prevalence globally
About 1.5 billion people, or 24% of the world's population, are infected with soil-transmitted helminths worldwide. Infections are fairly widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions
Propagation
Earth-transmitted earthworms are transmitted via eggs and excreted in infected human faeces. Adult worms reside in the intestine where they lay thousands of eggs a day.
 . In areas where sanitation is not good, these eggs pollute the soil environment. This happens in the way:
. In areas where sanitation is not good, these eggs pollute the soil environment. This happens in the way:Eggs are attached to vegetables when they are not cooked, washed or peeled carefully;
Eggs are ingested from contaminated water sources;
Eggs are ingested when children play in contaminated grounds and then put their hands in their mouths when not washing their hands.
In addition, hookworm eggs are hatched in the soil, releasing larvae into a form that can penetrate our skin. People are infected with hookworms mainly because of barefoot infection on contaminated soil. to mature in the soil before they become able to contaminate
Impact on nutrition
Earthworms weaken human nutrition in many ways.
The worms take food from host tissues, including blood, which leads to blood loss and protein.
In addition, hookworm infection also causes chronic intestinal bleeding leading to severe anemia.
Worms increase the absorption of nutrients for the body.
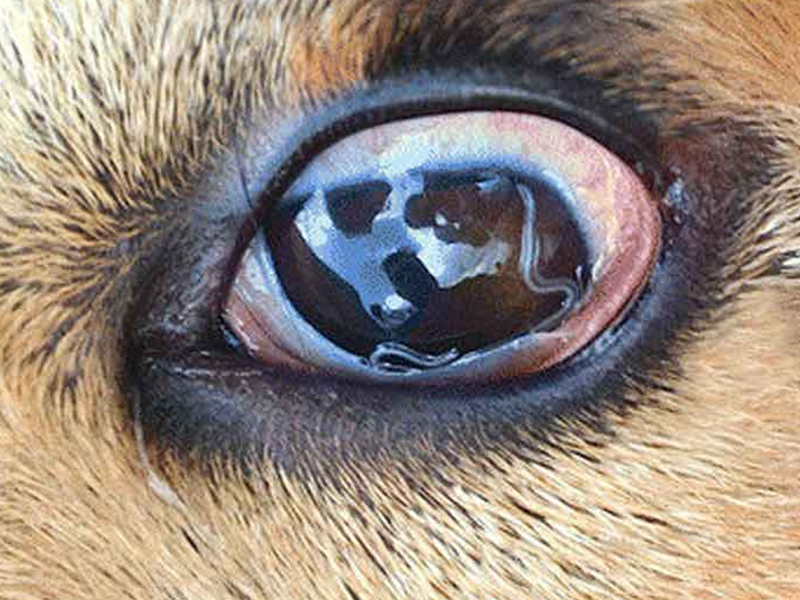 . In addition, roundworms can compete with vitamin A in the gut.
. In addition, roundworms can compete with vitamin A in the gut.Some earthworms reduce appetite, thus reducing nutrient intake and fitness. In particular, T. trichiura can make the digestive tract unbalanced and cause diarrhea, dysentery
Incidence and symptoms
Incidence is related to the number of resident worms. People with mild infections (few worms) usually do not get sick. Severe infections can cause a range of symptoms including intestinal manifestations (diarrhea and abdominal pain), malnutrition, or discomfort and physical weakness, and poor height and physical development. matter.
Severe infections can cause intestinal obstruction and need to be treated with surgery.
Prevention Strategy of the World Health Organization (WHO)
In 2001, participants at the World Health General Assembly unanimously passed a resolution (WHA54.
 .19) calling for circulating countries to start addressing worm infections seriously, especially schistosomiasis and worms transmitted through soil. The strategy to prevent soil-transmitted helminth infections is to control the situation through periodic treatment of those at risk of living in endemic areas Subjects at risk are:
.19) calling for circulating countries to start addressing worm infections seriously, especially schistosomiasis and worms transmitted through soil. The strategy to prevent soil-transmitted helminth infections is to control the situation through periodic treatment of those at risk of living in endemic areas Subjects at risk are:Children in kindergarten
Children of school age
Women of childbearing age (including women in the second and third trimesters and lactating women)
Adults in high-risk occupations such as tea pickers or miners.
WHO recommends periodic drug treatment (deworming) without prior individual diagnosis for all people living in endemic areas. Treatment should be carried out once a year when the prevalence of soil-transmitted helminth infections in the community is above 20%, and twice a year, when the prevalence of soil-transmitted helminth infections in the community is over 50%. This intervention will reduce the incidence of disease by reducing the burden of worm infection. Besides:
Health and hygiene education reduces transmission and reinfection by promoting healthy behaviors
The supply of adequate hygiene also. . Dịch vụ: Thiết kế website, quảng cáo google, đăng ký website bộ công thương uy tín
Related news
-
 Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ...
Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ... Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ...
Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ... Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ...
Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ... Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ...
Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ... Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ...
Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ... Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ...
Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ... MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ... CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...
CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...






