Worms And What To Know To Prevent Disease
Trichuris trichiura is a very common infection of the intestinal worms. This is the third largest worm infection in the world, with approximately 604–795 million people infected.
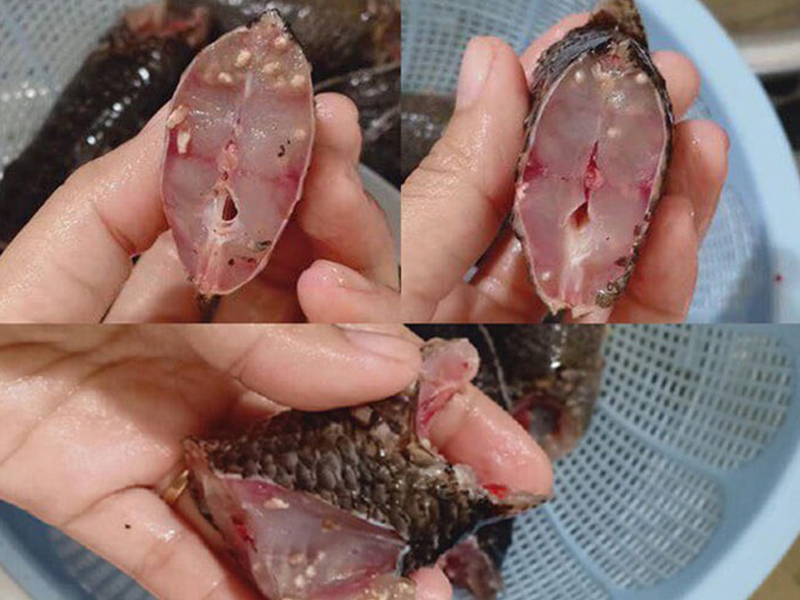
Hair parasitic worms in human intestines
Hairworm is the most common disease in tropical and subtropical countries including Vietnam. Human hairworm disease is spread mainly through diet and stool. Living hygiene can increase the risk of further illness
The most favorable environment for developing hairworm disease is hot and humid climate, unhygienic personal hygiene, backward lifestyle. People in rural areas are often more infected than people in urban areas, especially in areas with habit of using fresh fertilizer to fertilize fields.
Causes of Hairworm disease
The causative agent of trichuris trichiura hairworm
Hairworms are usually pale pink or milky white
Survival ability in the external environment: hairworm eggs have most of them having time to develop in the outside to be able to infect humans.
 . The time for eggs to develop into eggs carrying larvae is about 17 - 30 days in a temperature of about 25 - 300C, humidity is over 80% and must have oxygen. Hairworm eggs are more prone to damage under the influence of sunlight, with temperatures above 500C worm eggs will die.
. The time for eggs to develop into eggs carrying larvae is about 17 - 30 days in a temperature of about 25 - 300C, humidity is over 80% and must have oxygen. Hairworm eggs are more prone to damage under the influence of sunlight, with temperatures above 500C worm eggs will die.A female worm lays an average of 3,000-20,000 eggs a day, so the speed of the disease is very serious if it is not detected, diagnosed and treated in time.
The most common cause of people suffering from hairworm infection is by eating undercooked foods and drinking water containing hairworm eggs.
Where do hairworms usually live?
Worms often hide in soil, so if children play in areas where worms are found and accidentally bring their hands to their mouths, they are also more likely to become infected
Symptoms of Hair Worms
Depending on the level of infection, there will be different symptoms, namely:
Mild infection of the hair worm: most have no specific symptoms; Some cases may have symptoms such as nausea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, constipation, indigestion, headache
Severe infection of hairworms:
They will damage the intestinal mucosa in place, resulting in digestion that is similar to dysentery syndrome (abdominal pain, diarrhea, small stools per defecation and sometimes with little blood).
Causing anemia, abnormal recording, body weakness ...
 .
.Hairworms, when severe and prolonged, can cause rectal prolapse and secondary infection due to prolapse and ulceration of the rectum.
In rare cases, itching rash can occur.
When having one of the above symptoms, people should immediately go to the nearest hospital / health center to be examined, diagnosed and given timely treatment by specialists.
How is it transmitted?
The place where the hair worm is located is human
Incubation period: usually not clear. When humans ingest hairworm eggs, eggs will hatch into the small intestine, release larvae, larvae go through the intestinal wall and enter the bloodstream, they move to the alveoli and develop in the lungs, then go up trachea and swallowed back into the stomach. In the cecum, this larva develops into an adult hair worm. From the time the patient swallows eggs with larvae to the first symptoms in the lungs from 5-14 days.
The stage of transmission: is the period of life of the female worm when maturing from being fertilized. From swallowing eggs containing larvae to adult worms will lay eggs about 45 to 60 days.
 . The life cycle of hair worms can live from 5 to 6 years if untreated
. The life cycle of hair worms can live from 5 to 6 years if untreatedWho is at risk for Hairworm disease
Anyone can get trichuriasis if they ingest larvae or eggs. Meanwhile, childhood hairworm infections are very common because they often play in soil contaminated with worms and then put their hands in their mouths
Causes that increase the risk of hairworm infection include:
Handling faeces, waste water and garbage in contravention of hygiene regulations
Use fresh manure to fertilize and water plants
Eating and drinking are not hygienic
Direct contact with the environment with hairworm eggs.
Preventing hairworm disease
Regularly propagandizing and educating to raise people's awareness about food hygiene and safety, personal / community hygiene, protect the lips of people to prevent the risk of hairworm infection.
Building reasonable toilets. Must create for themselves a reasonable personal hygiene lifestyle: clean hands before eating and after going to the toilet
Eat boiled and boiled foods, limit eating raw vegetables before they are washed.
Do not use fresh manure to fertilize plants
Everyone should deworm worms once every 6 months.
Measures to treat Hairworm
Use single dose with high efficiency. However, the resistance of drugs due to indiscriminate use affects the effectiveness of worms. Depending on the severity of the disease, the doctor will prescribe appropriate medication for each patient to kill hairworms.
The treatment of hair worms. . Dịch vụ: Thiết kế website, quảng cáo google, đăng ký website bộ công thương uy tín
Related news
-
 Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ...
Parasitical Worms.com Tests to find the cause of urticaria, diagnosis of urticaria results will be available throughout the day. After the results the doctor will explain, point out the abnormal signs for your child to understand and he will prescribe medication for home. Question Hello doctor: I ... Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ...
Parasitical Worms.com Adult flukes are very small, 3 - 6 mm long, with 4 suction heads and a double hook, very short neck; coal consists of 3 segments, the final flukes have several hundred eggs, size 45 x 35 mcm, very similar to Toenia spp eggs. The disease is caused by the larva Echinococcus ... Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ...
Parasitical Worms.com Some diseases caused by larvae of the anisakinae family parasitize marine mammals. In humans, the parasite falls into a dead-end, or severe or severe illness depending on the place of parasite, number of larvae and tissue responses. Diagnosis is often difficult and the most ... Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ...
Parasitical Worms.com Illness caused by the nematode of Angiostrongylus cantonensis parasitizes and causes disease in the meninges, invasion of the brain can lead to death. Commonly called Meningitis - brain caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. The causative agent of nematode ... Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ...
Fascioliasis is two types of fascioliasis and small liver fluke. People are infected with food, skin. Flukes can cause hepatitis, liver tumors, liver necrosis, but fortunately, liver fluke can be cured if detected early, treated in a reputable facility with a good doctor, using drugs. Good, ... Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ...
Parasitical Worms.com Diagnosis is determined by seeing sparganum larvae from the wound. Clinical and prehistoric images of frog meat, eye-copying as well as the habit of eating undercooked snakes, mice, and eels are important factors for diagnosis. Doctor: Le Thi Huong Giang Medical Consultation: ... MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE (Aspergillus) 1. Epidemiology. Aspergillus fungus is one of the largest fungal strains, present in all over the world, there are about 100 species, currently there are about 20-30 species that cause disease in humans, important strains are A. fumigatus, A. flavus , A. niger such as ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Cryptococcosis (Tolurosis, European Blastomycois) 1. Etiology and epidemiology Cryptococcosis is also known as the European Blastomycose mycosis caused by Cryptoccocus neoformans, a thick cystic yeast, has serotypes A, D (C. neoformans var. Neoformans) and B, C ( C.neoformans var. ... MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ...
MUSHROOM DISEASE Sporotrichosis (Gardener Disease) 1. Epidemiology and etiology Sporotrichosis is a chronic disease caused by Sporothrix schenckii that causes damage to the skin or internal organs (also known as gardener disease - gardener's disease). This is a dimorphic mushroom. In nature, ... CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...
CANDIDA MUSHROOM 1. Germs Candidiasis is an acute, subacute or chronic disease caused by Candida-like yeasts, mostly Candida albicans. Candidiasis is available in the body (bronchus, oral cavity, intestine, vagina, skin around the anus) normally in non-pathogenic form. When having favorable ...







